FOCUS AREA - CHILD RIGHTS

Birth Registration
Birth registration is one of the most fundamental rights of a child; it is legal proof of a child’s identity. Registration of births is also necessary for a government’s policy making and planning. Pakistan does not have a universal system of birth registration. The Union Councils, responsible for birth registration lack capacity, while parents see little or no benefit in registering their children at birth.

Child Labor
Over 12.5 million children in Pakistan are involved in labor (ILO, 2012). The Global Slavery Index 2013 categorized Pakistan as the third highest in prevalence of child and forced labor despite a significant decline in other parts of the world. In Pakistan, children below 18 years of age are employed in physically demanding and exploitative work in different sectors including brick kilns, rag picking, mining, fishing and quarrying (UNICEF, 2011). Legislation and implementation is crucial to protecting the rights of children.

Violence Against Children
According to UNICEF, some of the most pervasive forms of violence against children include physical, psychological and sexual violence in homes, schools and places of work. In addition to the forms of violence against children mentioned above, some other forms in Pakistan include: child marriages, acid attacks, infanticide, and physical punishment in order to discipline children.

Street Children
According to the United Nations in Pakistan, an estimated 1.2 to 1.5 million children are thought to be on the streets of Pakistan’s major cities. These children are denied basic rights such as access to shelter, education, and healthcare, which makes them extremely vulnerable. They are at the risk of being drawn into abusive situations, including child labor, sexual exploitation, and trafficking.
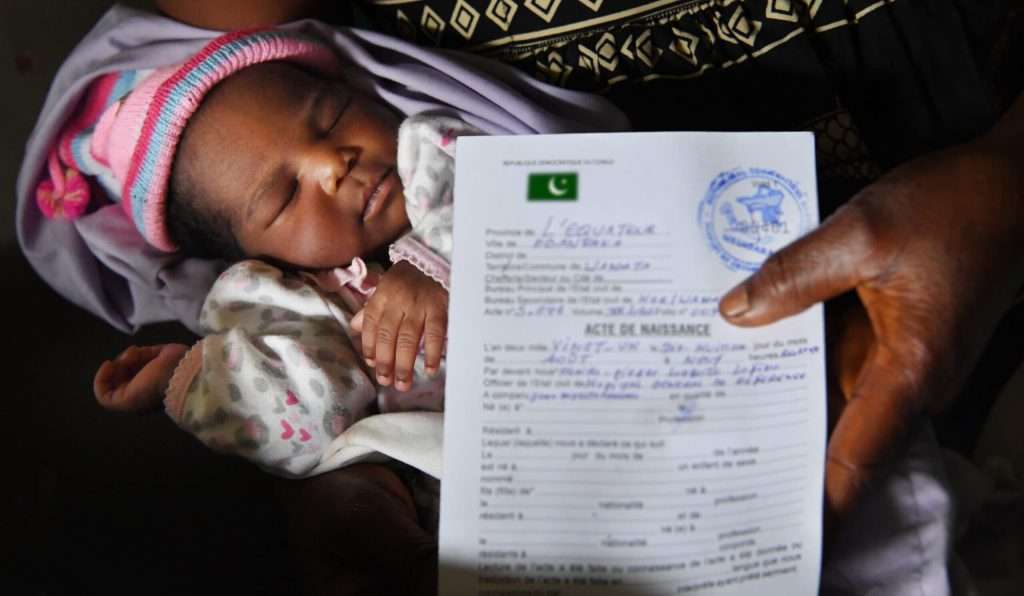

Birth Registration
Birth registration is one of the most fundamental rights of a child; it is legal proof of a child’s identity. Registration of births is also necessary for a government’s policy-making and planning. Pakistan does not have a universal system of birth registration. The Union Councils, responsible for birth registration, lack capacity, while parents see little or no benefit in registering their children at birth.
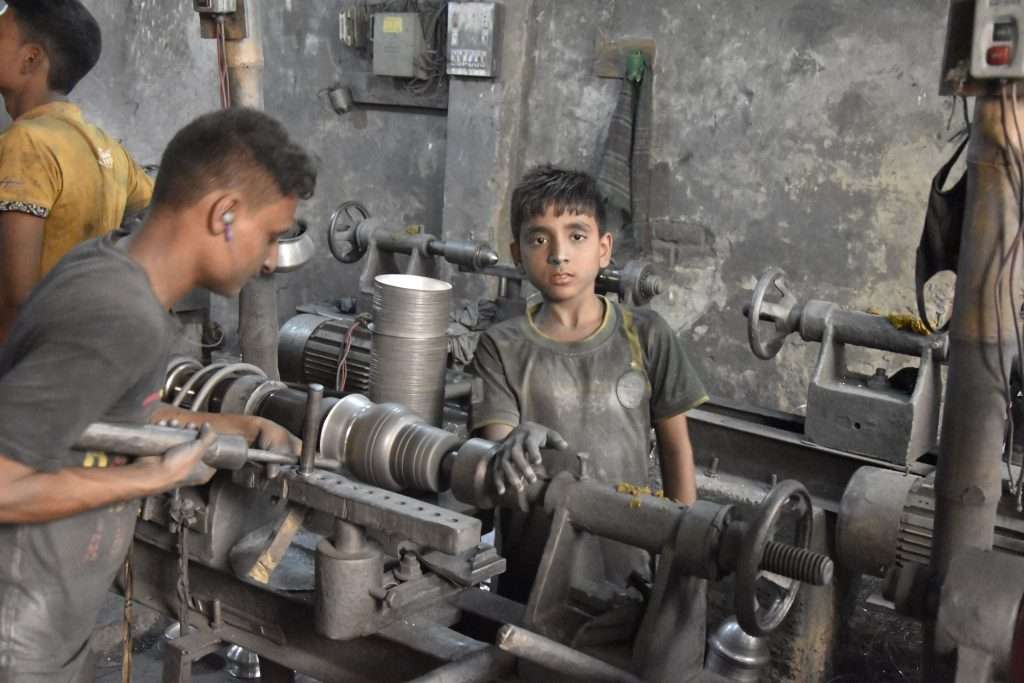

Child Labor
Over 12.5 million children in Pakistan are involved in labor (ILO, 2012). The Global Slavery Index ranked Pakistan eighth in child and forced labor despite a global drop. Brick kilns, rag picking, mining, fishing, and quarrying are among the industries in Pakistan where children under 18 labor in dangerous and exploitative conditions. (UNICEF, 2011). Child rights need legislation and implementation.
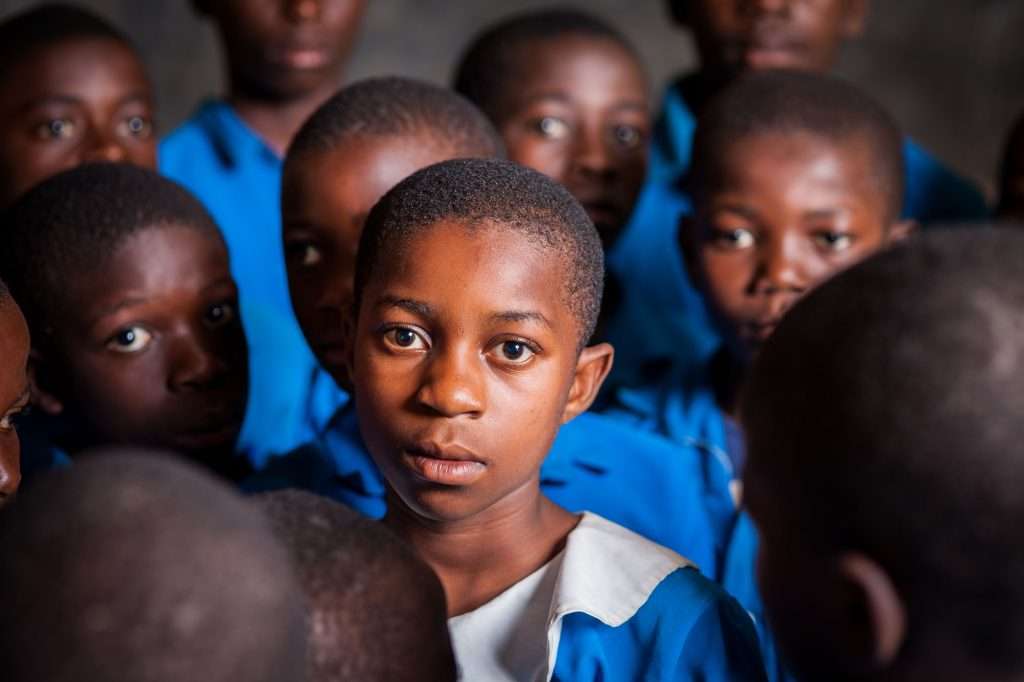

Violence Against Children
According to United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), some of the most pervasive forms of violence against children include physical, psychological, and sexual violence in homes, schools, and places of work. Apart from the types of violence against children mentioned above, Pakistan also has prevalent cases of child marriages, acid attacks, infanticide, and physical punishment to discipline children.
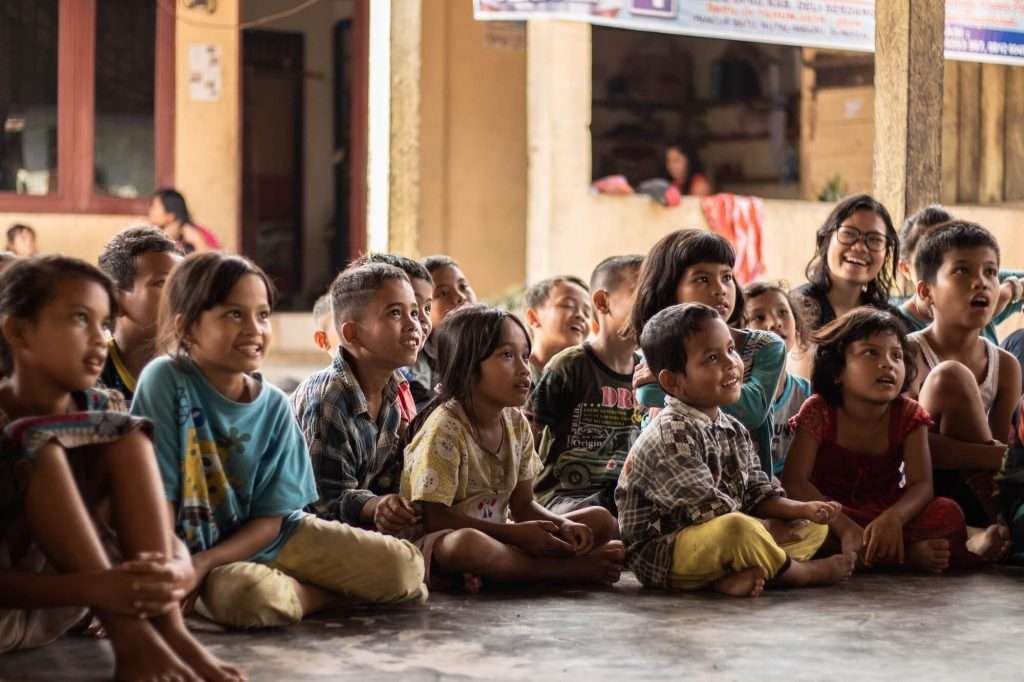

Street Children
According to the United Nations in Pakistan, an estimated 1.2 to 1.5 million children are thought to be on the streets of Pakistan’s major cities. These children are denied fundamental rights such as access to shelter, education, and healthcare, which makes them highly vulnerable. They risk being drawn into abusive situations, including child labor, sexual exploitation, and trafficking.

Constitution of Pakistan
The Constitution of Pakistan has incorporated provisions about the right to free & compulsory education in multiple Articles. Article 25A of the constitution highlights the fundamental right to education. The state must ensure that all children between the ages of five and sixteen receive free and compulsory education, as determined by law. Pakistan has officially endorsed the Universal Declaration on Human Rights (UDHR). Article 26 (1) of the UDHR recognizes that everyone has the right to education. Primary education must be accessible. Nevertheless, ratified international agreements in Pakistan do not have the force of law and must be implemented through legislative means.
Pakistan Vision 2025
Pakistan Vision 2025 aims to expand education levels and improve education quality substantially. A significant goal of Pakistan Vision 2025 is to raise the primary school enrollment and completion rate to 100% and the literacy rate to 90% by focusing on improving access to and the quality of Primary Education. Furthermore, it includes bringing the primary and secondary gender parity index to 1 and doubling the percentage of women in the labor force from 24% to 45%. To create a knowledge-based economy, the plan asks for a significant increase in public spending on higher education from 0.2% to 1.4% of GDP and a substantial increase in enrollment from 1.5 million to 5 million.

Sustainable Development Goals 2030
Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) is about quality education. SDG4 seeks “inclusive and equitable quality education and to promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.” SDG 4 has ten education-related goals. Seven of these goals describe the expected results, while the remaining three explain the way to achieve them. The ten goals include Universal Primary & Secondary Education, Early Childhood Development and Universal Pre-primary Education, Equal Access to Technical/Vocational and Higher Education, Relevant Skills for Decent Work, Gender Equality and Inclusion, Universal Youth Literacy, Education for Sustainable Development, Global Citizenship, Effective learning environments, Scholarships, and Teachers & Educators.

Constitution of Pakistan
The Constitution of Pakistan has mentioned child protection and safeguarding the child's rights in several of its Articles. On the other hand, children in Pakistan are still put in dangerous situations because of laws that are either inadequate or not enforced properly. Pakistan has ratified the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC). As per the Convention's Article 37(a), subjecting any child to torture or any other form of cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment is prohibited. However, ratified international instruments do not have the force of law in Pakistan; they must be incorporated through legislation.

Pakistan Vision 2025
As part of their vision for the future, Pakistan's leaders have set the goal of increasing primary school enrollment to 100% and the literacy rate to 90% by 2025. The Vision 2025 initiative has pledged to decrease the rate of infant mortality from 74 to below 40 per 1,000 births and lower maternal mortality from 276 to less than 140 per 1,000 births. Vision 2025 aims to fulfill all provisions outlined in Article 38 of the Pakistani Constitution pertaining to children's rights. This involves advocating for an inclusive education system that accommodates students with disabilities and proactively enacting policies for Children.

Sustainable Development Goals 2030
Though the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development has not included any child rights goal, it is inextricably linked to human rights and children's rights specifically. Children are affected by all the SDGs, whether poverty (Goal 1), hunger (Goal 2), health (Goal 3), education (Goal 4), gender equality (Goal 5), climate change (Goal 13), or violence against children (Goal 16.2). Even SDGs that don't specifically reference children's rights help their achievement. UNICEF identified 44 SDGs that have a direct impact on children. Children's rights and well-being must be prioritized in the SDGs. It may accelerate sustainable growth by ending poverty and isolation.